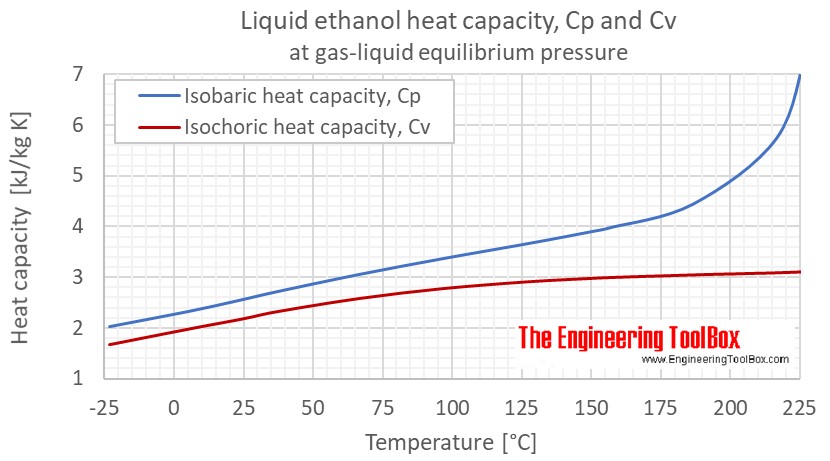
Cp And Cv Of Water
Compressed water properties specific volume enthalpy and entropy of compressed water.
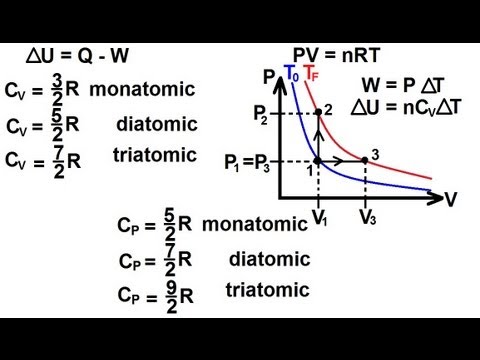
Cp and cv of water. A correct answer will be greatly appreciated. Heat capacity is an extensive propertythe corresponding intensive property is the specific heat capacitydividing the heat capacity by the amount of. Air specific heat at constant temperature and varying pressure figures and table showing isobaric cp and isochoric cv specific heat of air at constant temperature and varying pressure ranging 001 to 10000 bara. In this article we will discuss two types of molar heat capacity c p and c v and derive a relationship between cp and cv.
The si unit of heat capacity is joule per kelvin jk. If you are asking about g for water vapor then a first approximation would be to assume water v. Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to a given mass of a material to produce a unit change in its temperature. At constant volume the molar heat capacity c is represented by c v.
In general both cp and cv depend on temperature and therefore so will cpcv g. The molar heat capacity c at constant pressure is represented by c p. H2oh2486112625 i would at least like the cv and cp values for water vapor at 2755 k. What phase of water gas liquid or solid and at what temperature.
What are heat capacity c c p and c v. Density water dynamic viscosity water kinematic viscosity water specific inner energy water specific enthalpy water specific entropy water specific isobar heat capacity cp water specific isochor heat capacity cv water thermic conductivity water speed of sound water. The following thermodynamic properties are calculated. I need to find out the cpcv value for water vapor and hydrogen gas at 2755 k and a molar ratio of.
Heat capacity relation between cp and cv the molar heat capacity at constant pressure cp is always greater than the heat capacity at constant volume cv because when heat is added to the constant pressure there is always an expansion in the substances. In thermal physics and thermodynamics the heat capacity ratio also known as the adiabatic index the ratio of specific heats or laplaces coefficient is the ratio of the heat capacity at constant pressure c p to heat capacity at constant volume c vit is sometimes also known as the isentropic expansion factor and is denoted by g for an ideal gas or k the isentropic exponent for a.