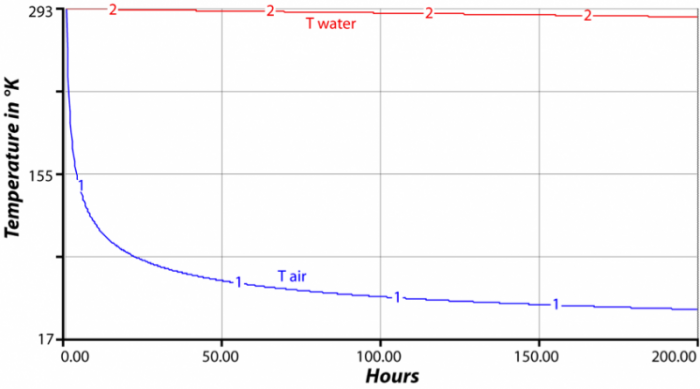
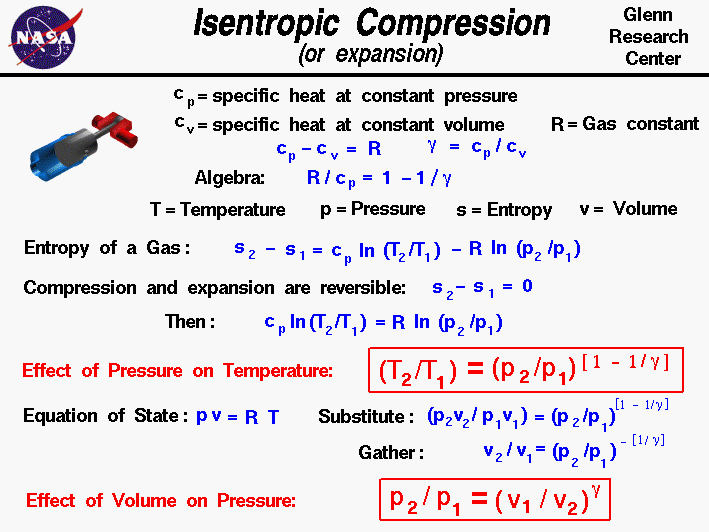
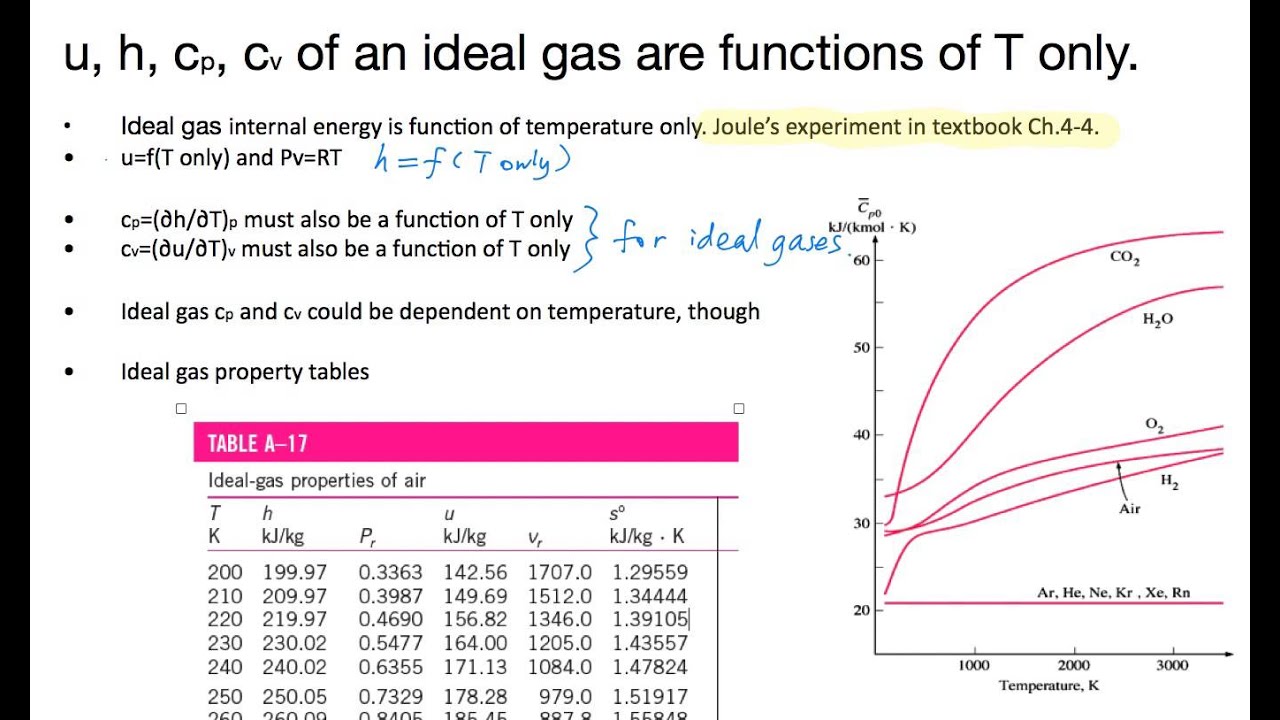
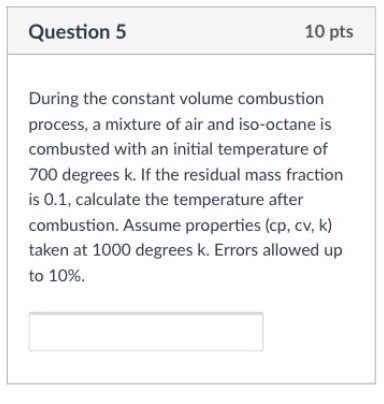
Cp And Cv Of Air At Different Temperatures
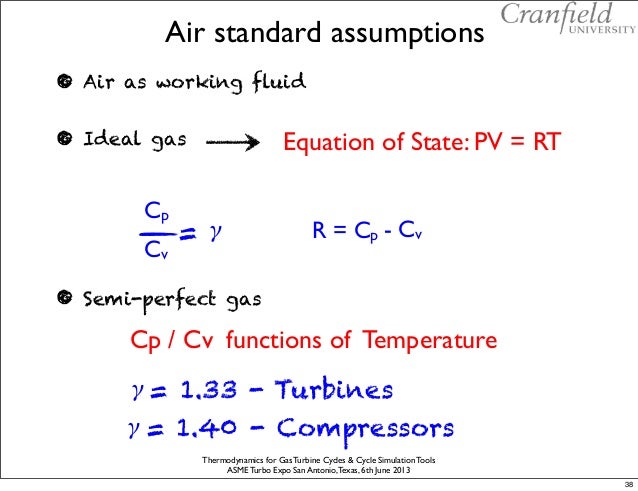
For air gamma 14 for standard day conditions.
Cp and cv of air at different temperatures. An ideal gas with specific heats independent of temperature and is referred to as a perfect gasfor example monatomic gases and diatomic gases at ordinary temperatures are considered perfect gases. Figures and table showing isobaric cp and isochoric cv specific heat of air at constant temperature and varying pressure ranging 001 to 10000 bara sponsored links specific heat c is the amount of heat required to change the temperature of a mass unit of a substance by one degree. In this article we will discuss two types of molar heat capacity c p and c v and derive a relationship between cp and cv. Where and have been used to denote the specific heats for one kmol of gas and is the universal gas constant.
The ratio between cp and cv is the specific heat ratio g. G cp cv. The molar heat capacity c at constant pressure is represented by c p. However they are all functions of temperature and with the extremely high temperature range experienced in internal combustion and gas turbine engines one can obtain significant errors.
Cv is the amount of heat energy that a substance absorbs or releases per unit mass with the change in temperature where a volume change does not occur. Properties of various ideal gases at 300 k gas. The nominal values used for air at 300 k are c p 100 kjkgk c v 0718 kjkgk and k 14. In thermal physics and thermodynamics the heat capacity ratio also known as the adiabatic index the ratio of specific heats or laplaces coefficient is the ratio of the heat capacity at constant pressure c p to heat capacity at constant volume c vit is sometimes also known as the isentropic expansion factor and is denoted by g for an ideal gas or k the isentropic exponent for a.
Gamma cp cv gamma is just a number whose value depends on the state of the gas. At constant volume the molar heat capacity c is represented by c v. What are heat capacity c c p and c v. Specific heat at const.
There is an equation to. At higher temperatures the difference between cp and cv in solids is not so small. However it is not easy to measure cv of solids because of the increasing pressure. Cp cv r.
Difference between cv and cp definition. Where r is the universal gas constant. We can define an additional variable called the specific heat ratio which is given the greek symbol gamma which is equal to cp divided by cv. Online calculator figures and tables showing how specific heat cp and cv of dry air vary with temperature at different pressures si and imperial units sponsored links specific heat c is the amount of heat required to change the temperature of a mass unit of a substance by one degree.